Prof. Gangfeng Ouyang’s group at School of Chemistry made important achievements in the field of advanced oxidation processes: An unprecedented non-photo mediated hole (h+) oxidation system
Source: School of Chemistry
Edited by: Tan Rongyu, Wang Dongmei
Photoinduced holes (
h+) generated on heterogeneous catalysts could serve as critical active oxidative species in splendid applications, including green energy exploration, chemical synthesis and environmental technology. As the core of photocatalytic activities, the electron-hole separation, transfer and recombination often take place in an ultrasmall timescale from tens of fs to hundreds of ps, which result in the low utilization of photoexcited electrons and holes. For decades, tremendous efforts have been made to increase the separation efficiency of photoexcited electron-hole pairs, via facet/defect engineering or heterojunction construction on the catalysts. Even so, still a majority of carriers are consumed by charge recombination prior to surface reactions.
Inspired by the researches of sensing field, a research team led by Professor Gangfeng Ouyang of the School of Chemistry at Sun Yat-sen University proposed a facile strategy-utilizing defective carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and strong electron-accepting superoxides to fabricate holes with high oxidative capacity and long lifetime. This is the first time to construct a non-photo mediated hole oxidation system, which exhibited striking catalytic performances for the degradation of organic pollutants, much higher than those of reported photocatalysts. This work provides new ideas for the construction of systems with long-lived carriers.
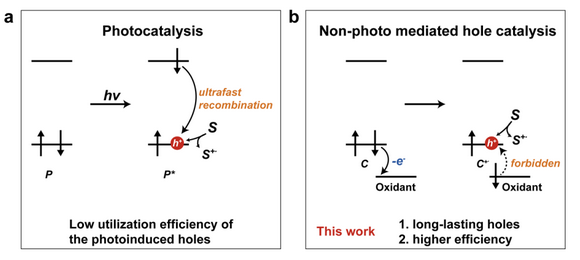
Figure 1. Functional principles of electron transfer in (a) light-induced photocatalytic system; (b) Proposed non-photo mediated hole catalytic system.
A deep study revealed that the intrinsic defects with unpaired spins on CNTs served as adsorptive sites to activate superoxides. Moreover, theoretical results demonstrated that the redox potential of this system could be tuned by proper defect construction on CNTs, rendering it significantly outperformed the classical oxidation processes for selective target pollutants elimination in actual wastewater. Furthermore, the defective CNTs were fabricated in-situ into membranes, which could treat the organic pollutants in a continuous flow mode.
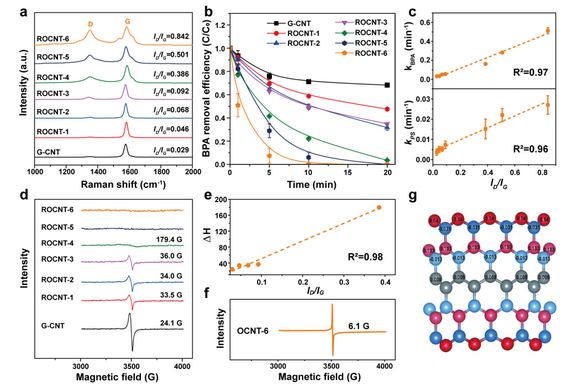
Figure 2. Characterization of defective CNTs and catalytic performance of the CNT/PS system for organic pollutants degradation.
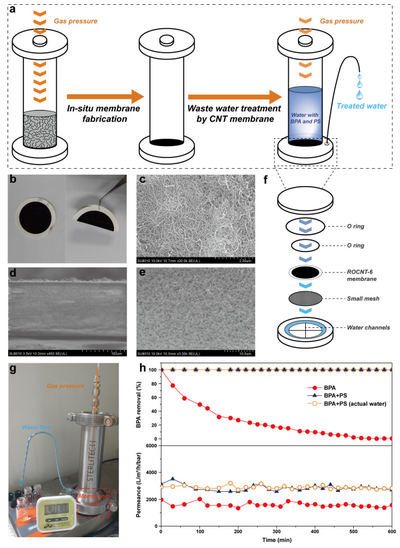
Figure 3. Membrane fabricated in-situ and wastewater treatment in a continuous flow system.
The research work has been published in
ACS Central Science entitled “Unprecedented Nonphotomediated Hole (
h+) Oxidation System Constructed from Defective Carbon Nanotubes and Superoxides”.
The first author is Dr. Junhui Wang, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-sen University. Professor Gangfeng Ouyang (Sun Yat-sen University) is the corresponding author. This work was supported by the Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China, Guangdong Provincial Key R&D Programme, the NSF of Guangdong Province and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Link to the paper:
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acscentsci.0c01600
