Prof. Gangfeng Ouyang’s group at School of Chemistry made important achievements in the field of photosynthesis of hydrogen peroxide
Source: School of Chemistry
Edited by: Tan Rongyu, Wang Dongmei
Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) are widely applied to the treatment of refractory organic pollutants in the environment. However, the continuous addition of oxidant limits their application in in-situ remediation of river courses. Hydrogen peroxide (H
2O
2) is the most commonly used oxidant in AOPs. Photosynthesis of H
2O
2 is a promising approach to provide oxidants for AOPs in an in-situ and continuous way. However, limited by the rapid charge recombination, organic electron donors and O
2 atmosphere are usually required.
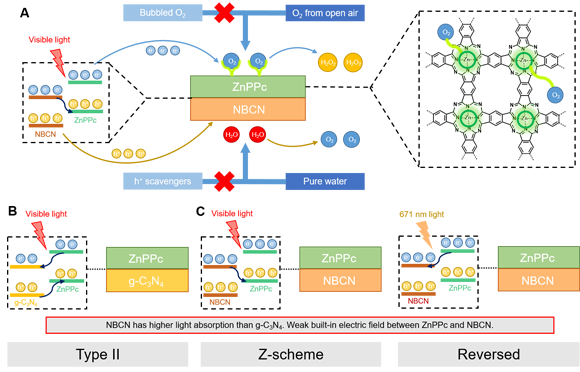
Figure. (A) Pathways for the photosynthesis of H
2O
2 from H
2O and O
2. (B) Electron transfer in ZnPPc-g-C
3N
4 under visible light illumination. (C) Electron transfer in ZnPPc-NBCN under visible light or monochromatic light illumination.
Recently, a research team led by Professor Gangfeng Ouyang of the School of Chemistry at Sun Yat-sen University designed a new photocatalyst for photosynthesis of H
2O
2. The photocatalytic rate of as high as 114 μmol g
-1 h
-1 for the production of H
2O
2 in pure water and open air is achieved by using a new Z-scheme heterojunction, which outperforms almost all reported photocatalysts under the same conditions. A deep study at atomic level demonstrates for the first time that Z-scheme electron transfer is realized by improving the photoresponse of the oxidation semiconductor under visible light, when the difference between the Fermi levels of the two constituent semiconductors is not sufficiently large. Moreover, it is verified that a type II electron transfer pathway can be converted to the desired Z-scheme pathway by tuning the excitation wavelengths. This study demonstrates a new feasible strategy for developing efficient Z-scheme photocatalysts by regulating photoresponses.
The research results have been published in
Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (
PNAS) entitled “Highly Efficient Photosynthesis of Hydrogen Peroxide in Ambient Conditions”. The first author is Dr. Yu-Xin Ye, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-sen University. Professor Gangfeng Ouyang (Sun Yat-sen University) is the corresponding author.
This work was supported by the Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China, Guangdong Provincial Key R&D Programme, the NSF of Guangdong Province and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Link to the paper:
https://www.pnas.org/content/118/16/e2103964118
